Thymalin peptide Usage, Dosage, Benefits and Side-effects
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Usage
- Thymalin: Potent Immunostimulant Medicine
- How Thymalin functions?
- Benefits of Thymalin
- Boosting Potential and Promising Health Benefits
- What role does Thymalin Peptides play in weight loss?
- What are the side effects of thymine?
- Dosage
- How to administer it?
- What are the differences between Thymalin and Thymesin Alpha-1?
- Conclusion
Molecular formula: c33h54n12o15
Molecular weight: 858.9 g/mol
Pubchem: Cid 3085284
Cas number: 63958-90-7
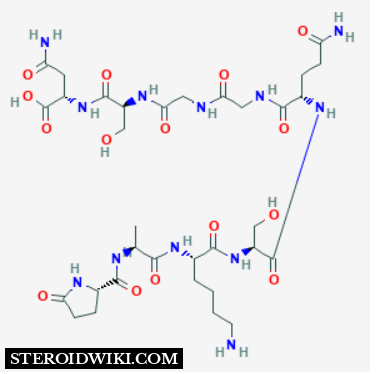
Sequence: Pyr-Ala-Lys-Ser-Gln-Gly-Gly-Ser-Asn
(NOTE: There is some debate on the internet about the difference between "Thymalin" and "Thymalin." Some people use the names interchangeably, while others insist the two names represent a different peptide — one consisting of the peptide sequence "H-L-Glu-Trp-OH" — and therefore carry out various functions. This article will continue to use "Thymalin" the peptide spanning nine amino acids)
What is Thymalin?

Thymalin is a mix of peptides from the thymus that can help regulate immune function and support the body’s natural ability to fight infections. It is also neuroprotective, anti-aging, and may protect against all-cause mortality. Thymalin is a synthetic peptide consisting of 32 amino acid-building units. It resembles the structure of thymosin alpha 1, a natural hormone our thymus gland produces that aids our immune system.
Structural Formula
Usage
Thymalin helps the body by enhancing the immune system and managing hormone synthesis. Because Thymalin is already a component of our immune system, it activates cell-mediated immunity, which protects us from hazardous chemicals. It also aids in phagocytosis, which is the process by which hazardous particles are cleaned out, as well as regeneration and hematopoiesis, which are processes by which our bodies recover and manufacture blood cells.
Thymalin: Potent Immunostimulant Medicine

Thymalin is used in medicine as an immunostimulant, which helps enhance the immune system. It is administered to help persons with inflammatory disorders, burns, trophic ulcers, or who have received therapies such as radiation and chemotherapy. It can also be administered before surgery to avoid complications that may arise after the procedure. Thymalin is a hormone the thymus gland produces that is vital to our immune system. One of its primary functions is to assist T-cells in growing and becoming robust. These T-cells work as our body's defenders, battling viruses, germs, and cancer cells to keep us healthy.
How Thymalin functions?
Thymalin stimulates the production of additional beneficial cytokines that regulate the immune response by binding to a receptor on the surface of T-cells. Biological activity can be restored naturally, and endogenous peptides have a low toxicological profile, which is the foundation for this theory. According to research findings, the drug's active ingredient, polypeptide, has been demonstrated to promote the recovery of physical activity.
Thymalin, a combination of peptides from the thymus, can control immunological response and aid the body's defence mechanisms against infections. Additionally, it possesses neuroprotective and anti-ageing characteristics that may help prevent many causes of death and lengthen longevity.
The active ingredient in Thymalin is a polypeptide coupled with salts that are water soluble as the carrier. According to research, Thymalin's immunostimulant effects are caused by the polypeptide's capacity to balance the subpopulations of functioning immune-competent cells.
Benefits of Thymalin
A peptide produced by the thymus gland that controls the immune system is called thymalin. It has been investigated for its potential applications in several sectors. According to reports, thymalin can be used in the following ways. Thymalin is a well-known potent immunomodulator in the human body. Below are a few benefits of using thymalin peptides.
1. Effective Immune Booster
It is believed to enhance the function of immune cells like T lymphocytes, which are crucial for immune response and infection defence. Thymalin may aid in regulating immune cell proliferation, differentiation, and activation, promoting overall immune system health.
Immune state
- Increased in previously anergic, immunosuppression, and older patients' blood lymphocytes and T cells.
- Increased immunological response to thymus-dependent antigens.
- Increased delayed-type hypersensitivity.
- Increased mitogen response by lymphocytes
- Increased production of M1F, IFN, IL-2, and GM-CSF by lymphocytes
- Decreased production of proinflammatory cytokines
- Increased chemotactic response by neutrophils
Clinical condition
- Improved inflammatory response and tissue repair.
- Improved host defence against infection
- Improved hemopoiesis, blood coagulation, and microcirculation
2. Anti-aging properties
Thymalin has been studied for its anti-aging qualities. It is supposed to rejuvenate the thymus gland, which shrinks and becomes less effective as we age. Thymalin may help maintain a more robust and functional immune system by promoting thymus function, thereby contributing to good ageing.
3. Wound healing
Thymalin has shown potential in wound healing experiments. It may improve tissue healing and regeneration by promoting skin cell migration and proliferation. Various mechanisms, including immunomodulatory characteristics and collagen synthesis stimulation, might mediate Thymalin's effects on wound healing.
4. Stress resistance
Thymalin has been studied for its capacity to boost stress tolerance and adaptation. It may aid in stress response regulation by controlling the production of stress-related hormones and enhancing the body's ability to cope with stress.
Immune-Boosting Potential and Promising Health Benefits
Thymalin has been demonstrated in studies to boost our immune system, allowing us to withstand infections better and improve our general health. Thymalin also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant characteristics, which may help to reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and cancer. The ongoing study looks into its potential for treating autoimmune diseases, cancer, and chronic infections.
Some people use Thymalin as a dietary supplement to help their immune systems and stay healthy. Nonetheless, further research and studies are required to acquire a thorough knowledge of the advantages and possible hazards of Thymalin use.
What role does Thymalin Peptides play in weight loss?
Thymalin peptide contains both pro- and anti-inflammatory effects, making it an effective anti-obesity therapy. Proinflammatory cytokines induce inflammation, while anti-inflammatory cytokines inhibit it.
There is an imbalance of these two kinds of cytokines in obesity, which can contribute to chronic inflammation. Thymalin peptide aids in the restoration of this equilibrium and the reduction of inflammation. Thymalin peptide may be worth investigating if you are obese and seeking a novel strategy to reduce weight.
What are the side effects of thymine?

Thymalin may have unintended consequences. Before taking Thymalin or any other experimental or off-label medicine, it is essential to consult or speak with a knowledgeable healthcare provider who can better guide you on its dosage and other relevant information.
Its usage has various beneficial effects, including better recovery, decreased inflammation, and increased flexibility. The peptide works highly well in assisting the rehabilitation of delayed healing injuries, such as those to connective tissue, such as tendons and ligaments. Muscle injuries and skin injuries are also considerably aided. According to reviews from its users and academics worldwide, it has very few, if any, significant adverse side effects.
When most peptides are injected, they might cause lightheadedness or nausea. Flu-like symptoms are also common among numerous other peptides. However, these undesirable side effects with Thymalin administration have been observed to be extremely minimal, if at all. Users will tolerate the peptide.
Before taking Thymalin or any other experimental or off-label medicine, speaking with a knowledgeable healthcare provider is essential. The following are some adverse effects of Thymalin.
Allergic reactions
Some individuals may experience allergic reactions, such as skin rash, itching, swelling of the face, lips, or tongue, and difficulty breathing.
Local irritation
Injection site reactions, such as redness, pain, or swelling at the injection site, may occur.
Nausea and vomiting
Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal disturbances, including nausea and vomiting.
Headache
Headaches have been reported in some cases.
Dizziness
Some individuals may experience dizziness or lightheadedness.
Fatigue
It causes fatigue, or feelings of tiredness may occur.
Flushing
Some individuals may experience skin flushing or redness.
Elevated body temperature
Thymalin might cause a mild increase in body temperature in some individuals.
If you feel these side effects, you should talk to a healthcare expert who can provide personalized advice based on your medical history and current health state. Always follow the dosage instructions and guidance of a certified healthcare expert.
Dosage
Immune disorders
Thymalin has been used for treating immune conditions, 0.5-1 mg/day doses.
Anti-ageing effects
Thymalin has been used for its anti-ageing products, 2-5 mg/day.
Facial wrinkles
Thymalin was administered at a dose of 2 mg/day for three months to individuals with facial wrinkles, and skin elasticity improved significantly.
Generally, 5-10 mg of Thymalin should be injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously once per day for ten days straight, with the treatment repeated every 6-12 months as needed.
Treating immunity disorders
Dose to be given for 3-10 days, depending on the severity of disease (repeat the course after 1-6 months if necessary)
- Children age 0-1 years: 1 mg per day
- Children age 1-3 years: 1.5-2.0 mg per day
- Children ages 4-6 years: 2-3 mg per day
- Children ages 7-14 years: 3-5 mg per day
- Adults: 5-20 mg per day (30-100 mg total per course)
Prevention
5-10 mg per day for adults
1-5 mg per day for children
How to administer it?
It is delivered via intramuscular injection.
What are the differences between Thymalin and Thymesin Alpha-1?

Thymalin and Thymosin Alpha-1 (also known as Thymosin 1) are two peptide hormones the thymus gland produces. While they both have immune-modulating capabilities, their structures and functions differ. Thymalin and Thymosin Alpha-1 differ in the following ways:
Differences in terms of structure
Thymalin is a peptide comprising two subunits, Thymalin A and Thymalin B, that come from the same precursor molecule. Thymosin Alpha-1, on the other hand, is a single 28-amino acid peptide chain.
Differences in terms of Origin
Thymalin is primarily synthesized and secreted by the thymus gland's epithelial cells. Although located in the thymus, thymosin Alpha-1 is produced by the enzymatic cleavage of a giant precursor molecule, prothymosin alpha.
Differences in terms of Function
Thymalin is involved in immune regulation and has been demonstrated to improve T lymphocyte function, which is required for immunological responses. It contributes to regulating immune cell proliferation, differentiation, and activation. Thymosin Alpha-1 likewise affects the immune system, although its effects are broader. It boosts the immune response to infections by stimulating the creation and maturation of different immune cells.
Differences in terms of Clinical applications
Thymosin Alpha-1 has been intensively researched for its possible therapeutic uses in various illnesses, including viral infections (such as hepatitis B and C, HIV), cancer, and immunodeficiency disorders. It has been used as an immunomodulatory drug and adjuvant treatment in rare situations. Although it has received less attention, Thymalin has shown promise in wound healing, neuroprotection, and stress management.
Differences in terms of Clinical accessibility
Thymosin Alpha-1 is an FDA-approved medicine used in clinical trials in several countries, mainly for treating persistent viral infections and immunodeficiency diseases. Thymalin, on the other hand, is mainly employed in research settings and is not yet generally accessible for clinical usage.
The clinical uses may differ as both Thymalin and Thymosin Alpha-1 have demonstrated potential advantages in research.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Thymalin, a synthetic peptide with immunostimulant and healing properties, has shown benefits such as better recuperation and decreased inflammation. It appears well-tolerated by users, with few reported adverse side effects. Before considering Thymalin or any other experimental drugs, it is crucial to seek guidance from a qualified healthcare professional to ensure safe and appropriate usage. Thymalin research continues to reveal its therapeutic potential, providing promise for effectively treating various health issues.
Click here to read more about Peptides.
Disclaimer: SteroidWiki doesn’t promote unlawful usage of any chemical compound. The knowledge presented in this article and on the website is purely for educational purposes. If you intend to use the information provided in this article for any purpose, please make sure to check & comply with the laws of your country or area.