DSIP: Complete Profile, Dosage, Usage, and other relevant information
Table of Contents
- Empirical Formula
- Molecular Weight
- Amino acid sequence
- Introduction
- Content And Potency
- Recommended Dosage of DSIP
- What is Delta sleep-inducing peptide, and what does it do?
- Research On Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide
- Benefits of DSIP
- Below are two main benefits of DSIP
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide and its Clinical Uses
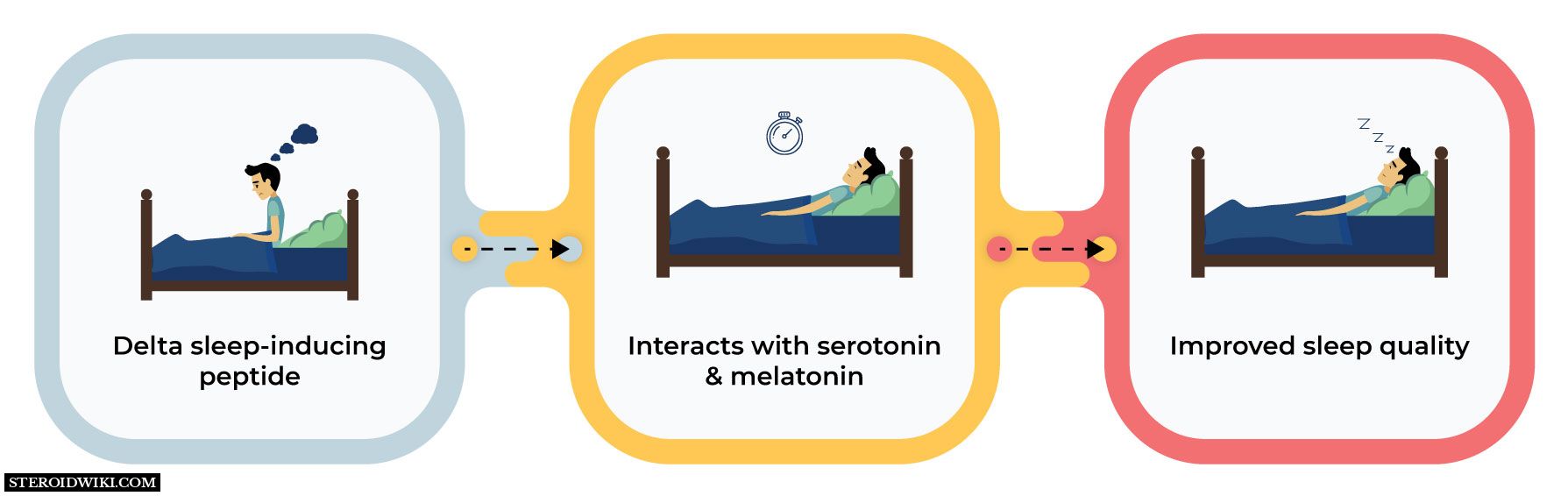
- Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide and Sleep
- Delta Sleep Inducing Peptide and its non-sleep effects
- Conclusion
Empirical Formula
C35H48N10O15
Molecular Weight
848.81
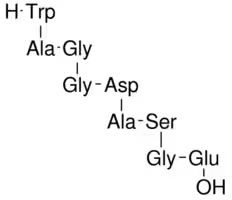
Amino acid sequence
Introduction

Delta Sleep Inducing Peptide (DSIP) is a well-known neuromodulator and naturally occurring nonapeptide that promotes sleep and has several other physiologic roles. It has been found to affect sleep regulation, wakefulness, and stress-related hormones. This peptide is becoming an increasingly popular way to support healthy sleep and overall well-being. It is often present in the brain as it quickly crosses the blood-brain barrier. It has been found and extensively researched for more than 40 years.
It has all been treated with poor sleep, pain issues, stress-related symptoms, low testosterone (by stimulating LH), and occasionally as an antioxidant and anti-cancer protein. It shows a strong stress preventive effect and lessens the metabolic and functional problems brought on by stress in humans and animals subjected to various pressures. Additionally, it has been demonstrated in studies to enhance hormone levels and physical performance.
This article will shed light on the overview of DSIP, Research, the potential uses and benefits, and provide information on possible side effects.
Content And Potency
It comes in a 3mL vial with a 1mg/mL subcutaneous injection concentration and efficacy.
Recommended Dosage of DSIP
The recommended dosage for DSIP to administer is 0.1mL subcutaneously once a day at night.
What is Delta sleep-inducing peptide, and what does it do?
The building elements of proteins, amino acids, are arranged in small chains called peptides. A particular kind of Delta sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP) has been investigated for its possible impact on stress and sleep.
DSIP has a calm and sleep-inducing characteristic, potentially increasing human growth hormone production. DSIP causes the pituitary gland to produce hormones, including oxytocin and cortisol, which aid in body and mind relaxation when used in moderation. According to studies, DSIP helps people sleep better and spend more time in deep sleep, the most healing stage of sleep. It could also boost daytime memory and alertness while lowering anxiety, sadness, and exhaustion. DSIP should only be used under the supervision of a licensed healthcare practitioner, even though it is thought to be safe when taken in low dosages.
Research On Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide

A naturally occurring compound, the Delta sleep-inducing peptide (DSIP), was first identified in a rabbit in 1977.
This nonpeptide chemical targets several locations, including the brainstem, and is produced in the hypothalamus.
The Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide, as suggested by its name, encourages sleep, as seen in:
- Rabbits
- Mice
- Rats
- Cats
- And even human beings.
Even better, it encourages a type of sleep known to cause an increase in the delta rhythm on the EEG.
Studies have demonstrated that DSIP, at modest dosages, can enhance sleep in various animals. Even though its physiological function is unclear, it again exemplifies numerous ideas that apply to brain peptides. These include:
- The intact blood barrier penetration
- The major effects following peripheral injection.
- The delayed and protracted time course
It is also relevant to others since it includes ideas one neuropeptide applies to others.
Let's attempt to talk about the research on the sleep-inducing peptide Delta.
A study was conducted in which 16 individuals with insomnia were investigated for the impact of the DSIP. In the lab, the participants were compelled to sleep for five nights in a row.
The definition for the evening's activity is as follows:
- The first night was for adaptation.
- The second night was for baseline measures.
The patients received 25nmol/kg body weight DSIP during the afternoon of the third, fourth, and fifth nights; half received a placebo.
Following that, the indicators of sleep structure, objective and subjective sleep quality, and level of fatigue were assessed. The objective sleep quality showed that DSIP was superior to the placebo in terms of sleep efficiency and sleep latency. Within the DSIP group, it was observed that a different subjective measure of perceived fatigue was declining.
Nevertheless, the data analysis indicated that the results may result from modifying the placebo group. It was determined that the short-term treatment of chronic insomnia is not a significant therapeutic advantage since no metrics demonstrated improvements.
Although it is present in many animals, DSIP encourages sleep in low amounts.
Benefits of DSIP
Here is a list of potential DSIP advantages:
- Restoring disturbed sleep patterns
- Promoting LH and GH release
- Lowering chronic pain, and
- Controlling cortisol production is all possible.
Below are two main benefits of DSIP
- Sleep Benefits
Instead of being a sedative, DSIP has been called a chemical that promotes sleep. When sleep is interrupted, there is a modulating influence on waking and sleep processes, and activity levels increase.
There are five phases of sleep, which may be divided into REM and NREM sleep. Numerous sleep aids alter the length or timing of these sleep periods. All these cycles are connected to critical physiological functions and the synthesis of anabolic hormones. DSIP does not alter sleep phases. It makes it easier to fall asleep and provides more restful sleep.
- Hormone Benefits
Anterior pituitary hormone release and neuroendocrine control are both regulated by DSIP. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and growth hormone (GH) production in humans is influenced by DSIP. It also affects how circadian rhythms are controlled.
The synthesis and control of hormones in these glands are improved by using DSIP. For instance, it reduces somatostatin synthesis and enhances LH and growth hormone production. The outcome is an increase in the synthesis of LH and GH and a decrease in the production of cortisol and somatostatin, two unwanted hormones.
Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide and its Clinical Uses
There are already clinical applications for DSIP. The treatment of alcohol and opioid withdrawal has been done using this substance. Following the injection of DSIP, clinical symptoms and indicators could go away.
However, some patients have mentioned experiencing the odd headache.
In research from 1986, rats' brain ventricles were even directly injected with the DSIP. The lack of increased sleep with the DSIP was attributed to the high metabolism. However, two analogs may promote sleep, while the third cause alertness.
It's helpful to note that in addition to providing sleep potential, it also provides sleep reversal within the DSIP analogs.
Delta Sleep-Inducing Peptide and Sleep
For a very long time, the mechanics of sleep have baffled scientists. For many generations, it has never changed.
Additionally, other substances have been suggested throughout the years to regulate sleep. These consist of the following:
- Cholecystokinin
- Prostaglandin l2
- Various unknown substances are labeled sleep-promoting substances.
It has been shown that most humoral mediators are related to sleep. For instance, it has an impact on arousal levels and circadian cycles. It is unclear whether the humoral mediator influences sleep patterns or merely responds to them. Only healthy subjects without sleep disorders have any effects from this peptide.
Delta Sleep Inducing Peptide and its non-sleep effects

DSIP has also been observed to exhibit distinct anticonvulsant effects in rats. The threshold for NMDA- and picrotoxin-induced convulsions is raised by the DSIP. This impact may change during the day, with nighttime showing a stronger antiepileptic action.
The ability to exhibit a daily shift in anticonvulsant action is not only to the DSIP. This ability is similar to how dexamphetamine, b-endorphin, and melatonin all lower the seizure threshold during the day. Additionally, the DSIP could only show one endogenous control on the brain's excitability.
Additionally, it has been seen to have neuroprotective effects in rats with bilateral carotid arteries strangled.
The DSIP also displays psychological and emotional reactions to stress.
Conclusion
DSIP can:
- Help induce better sleep.
- And relieve emotional and psychological responses to stress.
However, it is only advisable to provide DSIP after night. The dosage should be administered throughout the day to promote better sleep the following night and for several days after.
But remember that DSIP only has short-term advantages and is ineffective for managing insomnia over the long run.
Click here for more information on related topics.
Disclaimer: SteroidWiki doesn't promote unlawful usage of any chemical compound. The knowledge presented in this article and on the website is purely for educational purposes. If you intend to use the information provided in this article for any purpose, please make sure to check & comply with the laws of your country or area.