Oxytocin Acetate 2mg: Complete Profile, Dosage, and Other Relevant Information
Table of content
- Chemical Structure Depiction
- Molecular Formula
- Molecular Weight
- What is Oxytocin?
- The “Love Hormone”: Oxytocin’s Nickname
- How Does Oxytocin Work?
- Administration
- Dosage
- Suggested Frequency of Use
- Where to inject
- Suggested Injection Dosage per time
- What Type of water to mix with?
- How much water to add?
- Oxytocin components
- Roles of Oxytocin
- Benefits of Oxytocin
- Side effects
Disclaimer: SteroidWiki doesn't promote unlawful usage of any chemical compound. The knowledge presented in this article and on the website is purely for educational purposes. If you intend to use the information provided in this article for any purpose, please make sure to check & comply with the laws of your country or area.
Chemical Structure Depiction
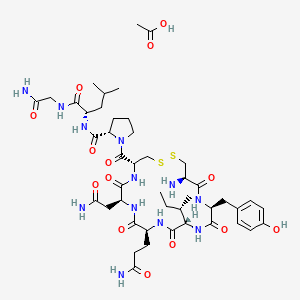
Molecular Formula
C45H70N12O14S2
Molecular Weight
1067.2 g/mol
What is Oxytocin?
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone consisting of Amino Acids. The hypothalamus produces it, while the pituitary gland secretes it. Oxytocin plays a significant function in the human body, particularly in women during pregnancy and nursing.
Oxytocin is the hormone that causes uterine contractions throughout pregnancy, especially during labor. Thus, oxytocin is frequently utilized in hospitals to help women with labor. When a mother begins nursing after giving birth, oxytocin is released to encourage lactation and cause milk to be produced. The positive feedback mechanism, which states that oxytocin is only produced when there is a trigger, causes oxytocin production to cease after the mother stops nursing.
Additionally, the release of oxytocin strengthens the important relationship between mother and child.
Oxytocin is frequently called the "love" hormone since it is released with any physical or sexual interaction. During sexual activity, oxytocin is released, allowing the pair to unwind and develop a stronger relationship. It regulates various social interactions and human behaviors.
The “Love Hormone”: Oxytocin’s Nickname
Oxytocin has a significant role in creating emotional attachments and social bonds, earning it the nickname "love hormone" often. Various physical interactions produce the hormone, including hugs, cuddles, and holding hands. Additionally, it is released during personal interactions like sexual contact, strengthening the emotional links between lovers.
According to research, oxytocin can strengthen the emotions of trust, empathy, and generosity, which makes it simpler for people to establish and keep social bonds. Due to this, it has gained general acceptance as an essential element in the formation and upkeep of human relationships, giving it the name of "love hormone."
Oxytocin, the “love hormone,” is crucial in various physiological and psychological processes, from childbirth and breastfeeding to social bonding and trust. As researchers continue to uncover the various functions and potential applications of oxytocin, this remarkable hormone is set to remain an important topic of conversation and study for years to come.
How Does Oxytocin Work?
The pituitary gland's axon terminals regulate pro-social actions like fear, reinforcement, and anxiety. These same axon terminals also serve as the bloodstream's primary route for oxytocin release. As a result, it has been hypothesized that these axons impact the brain effects related to behavior.
Another important point is that this peptide cannot reach the brain again after being released by the hypothalamus. This has led to the theory that the central projecting oxt neurons, which tend to be distinct from the neurons that go into the pituitary gland, are responsible for releasing the peptide that causes the behavioral consequences associated with its presence.
Consequently, oxytocin has been classified as serving substantial and intricate roles in the body and only evoking emotional reactions or arousal based on scientific studies on animal subjects. The "let down" reflex during lactation (breastfeeding) in females or pro-social attachment behaviors like bonding are a few of the key roles of oxytocin. The mood is also impacted.
The effects of oxytocin vary between men and women. When this peptide is present, females react to social cues more quickly than men.
Administration

Nasal spray, topical gel, vaginal cream, intravenous, and intramuscular solutions are among the several oxytocin dosage forms offered. The majority of intravenous solutions are utilized during labor and delivery in hospitals. Certain pharmacies produce nasal spray, topical gel, and troches that can be utilized for various ailments. Studies on the various formulations have indicated that nasal spray administration is effective quickly and lasts roughly an hour. Oxytocin levels in the brain were much greater following nasal administration than intravenous injection. Because it is directly absorbed into the body, intranasal administration is, therefore, most favored by doctors and may also be the most effective.
Dosage
The suggested dosage for vile size is 2mg
Suggested Frequency of Use
Once a day before bed
Where to inject
The injection is administered into the body fat surrounding the stomach area.
Suggested Injection Dosage per time
20-50mcg
What Type of water to mix with?
For this operation, you can utilize either sterile or bacteriostatic water. A minor quantity of a bacteriostatic substance, such as benzyl alcohol, is included in Bacteriostatic Water, which aids in preventing bacterial growth in the solution. On the other hand, Sterile water has been cleansed and germ-free.
Pick the right kind of water depending on your technique's particular needs and directions. If the instructions are unclear, get advice from a medical expert or adhere to the regulations set forth by the manufacturer or appropriate authorities.
How much water to add
2ml
How to Mix the Water and Peptide?
Draw 2 ml of water into the syringe with caution. The needle should now be inserted into the powder container. Don't shake the vial. It's vital to remember that. Instead, carefully turn the vial back and forth between your fingers to mix the powder completely.
Oxytocin components
The unit size and amount of the peptides are 2 mg per vial, respectively. It is a white powder that may be dissolved with 1% acetic acid or water. Lyophilized oxytocin can be stored for approximately three months at room temperature. It should be kept in a freezer set to -8°C when storing for an extended time. This peptide must be chilled at a temperature of no higher than 36F after being reconstituted.
Roles of Oxytocin
- Childbirth
- Sexual reproduction
- Potential muscle growth and Recovery
- Postpartum Recovery
Benefits of Oxytocin
Well-being
Oxytocin causes endocrine and physiological changes and a general sensation of well-being that includes serenity, enhanced social connections, higher trust, and decreased fear. Blood pressure decrease is another advantage in the long run.
Dysfunctional Sexuality
Sexual dysfunction can also be treated with oxytocin. According to research, long-term intranasal oxytocin treatment helped women's depressive symptoms and sexual function over time. More so in males than women, oxytocin boosted orgasm intensity and post-sex satisfaction. Men also demonstrated greater degrees of sexual satisfaction following sex with oxytocin. While others could empathize and share sexual wants, women felt more at ease.
Emotional Bonding
An emotional relationship with your partner, family, and peers is crucial. The lack of such a link may impact your general well-being. According to research, both treatment groups (oxytocin and placebo) reported experiencing an improvement in social responsiveness, quality of life, and capacity to form bonds with peers after the 2-week experiment. The two-week oxytocin therapy also decreased attachment avoidance and increased peer connection ratings.
Cognitive, Psychiatric and Behavioral Conditions
Due to its beneficial effects on socialization, oxytocin has been suggested to treat several cognitive disorders, including autism, social anxiety, and schizophrenia. Oxytocin has been proven to be beneficial for autistic children in more investigations. Young children with autism who received intranasal oxytocin therapy for five weeks had improvements in their social, emotional, and behavioral difficulties. Improvements in depression, PTSD, anxiety, hunger regulation, and weight reduction have been seen in other research.
Side effects
Following are the side effects that Oxytocin Acetate may cause
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Bleeding issues
- Cephalopelvic disproportion
- Cervical cancer, fetal problems,
- Prematurity, problems with uterine contractions (such as uterine atony, strong uterine contractions)
- Severe or unfavorable fetal position (such as transverse lies), or conditions that may necessitate a cesarean delivery (such as cord prolapse).
Other side effects
Oxytocin may cause serious side effects. Call your doctor at once if you have the following:
- A fast, slow, or uneven heart rate
- Excessive bleeding long after childbirth
- Blurred vision
- Severe headache
- Numbning in your neck or ears
- Severe weakness, Confusion, the feeling of low
Use with care if you have kidney illness. The effects might be amplified because this medication is removed from the body more slowly.
Click here for more information