IGF-1 Complete Profile, Dosage & Usage Guide
Table of Contents
Class of Compound
Peptide
Street Names
Somatomedin C
Chemical Structure
What is IGF-1?
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also known as somatomedin C, is a polypeptide hormone composed of 70 amino acids. Structurally, it shares homology with proinsulin and another factor called IGF-2. Disulfide bonds hold together the polypeptide chains of IGF-1. In the human body, IGF-1 is endogenously synthesized primarily in the liver. The production of IGF-1 is stimulated by Human Growth Hormone (HGH), which acts as a prohormone for IGF-1. The majority of the anabolic effects attributed to HGH are actually the result of downstream production of IGF-1.
Once produced, a significant portion of IGF-1 binds to Insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGF-BP), which greatly extends its half-life in the circulation. Although IGF-1 is produced throughout life, its levels peak during puberty. It is important to note that IGF-1 is not an anabolic steroid, but rather a protein hormone with a structure that closely resembles insulin, which is another peptide/protein hormone.
Mechanism of Action
IGF-1, a peptide hormone with anabolic properties, is released in response to growth hormone stimulation. This, in turn, inhibits the release of growth hormone through somatostatin, following a negative feedback mechanism. IGF-1 acts similar to insulin by exhibiting tyrosine kinase activity, which enhances glucose uptake in peripheral tissues. Additionally, IGF-1 activates the Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and PI3K signaling pathways, which sense nutrient availability and promote cell growth. Furthermore, IGF-1 also has the ability to delay apoptosis or cell death.
Variant of IGF-1
There are two distinct categories of IGF variants, namely IGF-1 LR3 and IGF-1 DES. IGF-1, due to its short half-life, is rapidly degraded by the body. To counter this, a modified form of IGF-1 called IGF-1 LR3 was developed, which contains an amino acid analog and has a prolonged half-life. On the other hand, DES IGF-1 is a truncated version of IGF-1 that is known to be up to ten times more potent than IGF-1. Despite their similarities to IGF-1, both IGF-1 LR3 and IGF-1 DES exhibit unique mechanisms of action, allowing them to function in distinct and specific manners.
What is IGF-1 LR3
IGF-1 LR3 is widely recognized as the most common and popular variant of IGF-1 utilized by bodybuilders and athletes today. With a half-life of approximately 20-30 hours, it surpasses the regular base IGF-1 in terms of potency. Its prolonged presence in the body allows it to effectively bind to cell receptors in muscle cells, leading to enhanced muscle growth throughout the day.
One of the major effects of IGF-1 LR3 is its ability to inhibit glucose uptake by body cells, which promotes fat burning and utilization of fat for energy production. Its extended duration of action, lasting nearly a day, has made it a preferred choice among patients and physicians alike, as it eliminates the need for site injections. IGF-1 LR3 cycles through the entire body, binding to muscle cell receptors and exerting its effects for approximately 24 hours, thus supporting a daily administration of the dosage.
IGF-1 DES

DES IGF-1, also referred to as DES(1-3)IGF-1, is recognized as a highly potent and fast-acting form of IGF-1. It is a truncated version of the base IGF-1 chain and is known to be five times more potent than regular IGF-1. However, due to its delicate nature, DES IGF-1 has a very short half-life of approximately twenty to thirty minutes. As such, it should be administered only at specific sites where muscle growth is desired.
DES IGF-1 is known for its ability to stimulate hyperplasia in muscles, which is the growth of new muscle cells, more effectively than IGF-1 LR3. It is best utilized for site injections rather than overall muscle growth due to its rapid action and short duration of activity.
In addition to its muscle growth-promoting effects, DES IGF-1 has the ability to bind to receptors in cells that have been affected by lactic acid, which is produced in higher amounts during intense training and vigorous activities. This unique characteristic allows DES IGF-1 to trigger tissue growth even during training, making it a favorable choice for athletes. DES IGF-1 can be used more frequently and for a longer duration compared to IGF-1 LR3, due to its shorter half-life.
IGF-1 Variant dosing
IGF-1
For optimal results, this particular variant of IGF-1 should be administered daily, seven days a week. It is recommended to take it after a workout session. Due to the short half-life of IGF-1, the risk of desensitization is minimal and rarely observed.
IGF-1 LR3
To ensure optimal usage, this specific variant of IGF-1 should be administered daily for seven consecutive days in a week. However, it is important to note that desensitization may occur, and the treatment protocol should not exceed a duration of 90 days. A break is necessary before considering a resumption of treatment.
DES IGF-1
For optimal results, DES IGF-1 should be dosed multiple times throughout the day, preferably before engaging in training activities. It is important to target specific sites and muscles with this variant. Due to its short half-life, desensitization is unlikely to be noticeable. To ensure precision, it is crucial to localize the injections to the intended target muscles. For example, if you wish to enhance your biceps, the injection should be administered directly into the biceps muscle. This approach allows for targeted and specific muscle growth.
Benefits of IGF-1
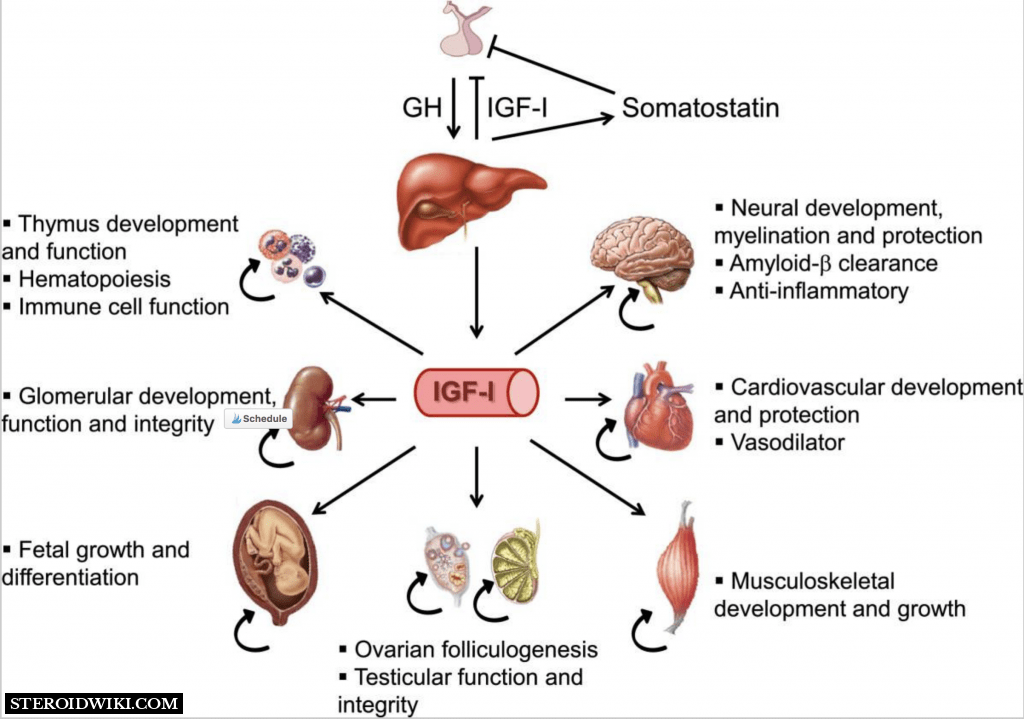
The advantages of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 (IGF-1) are as follows:
- Enhancement of protein synthesis in the body.
- Diversion of fat storage towards energy production, resulting in noticeable fat loss.
- Positive effects on metabolism, leading to increased lean body mass and reduced fat.
- Augmentation of regenerative properties of nerve tissues in the body.
- Upregulation of antioxidant benefits and strengthening of ligaments.
- Promotion of hyperplasia in muscle cells, resulting in fuller muscle tissues.
- Improved cognitive function.
Side effects IGF-1
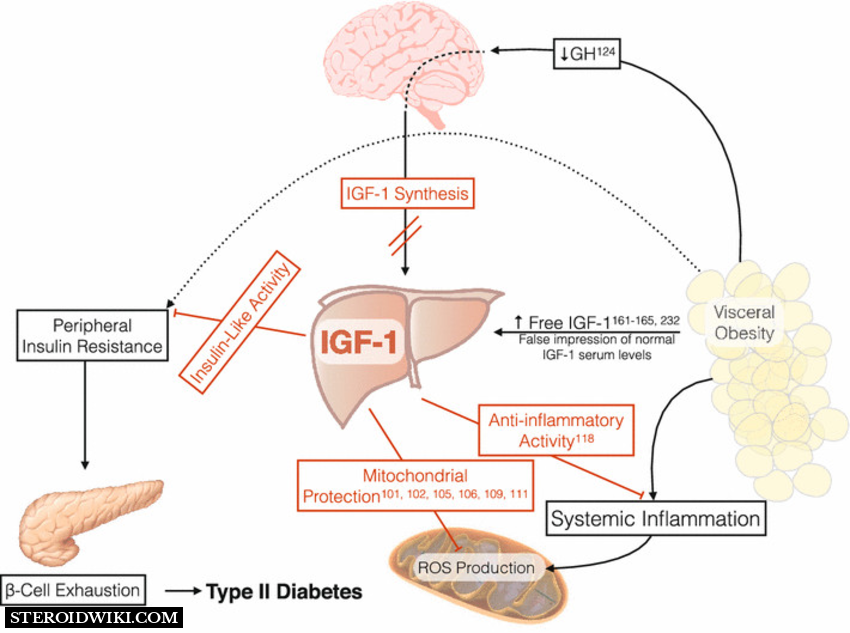
The administration of IGF-1 in high doses may result in hypoglycemia, although the severity is not as pronounced as that caused by insulin. This is the most common side effect associated with IGF-1 usage.
There is ongoing debate about whether IGF-1 can increase tumor size in cancer patients. While it is true that IGF-1 may have an impact on existing cancer cases, it does not directly cause cancer. In fact, IGF-1 is essential for regulating heart functions, stimulating brain cells, and improving nervous system functioning in the human body. However, it is important to note that IGF-1 can potentially cause severe blood sugar disorders, leaning towards hypoglycemia and diabetes, as well as growth in the organs of the digestive system, leading to a condition known as "bubble gut.
Administration
IGF-1 LR3 is available in two forms for administration: intramuscular (IM) or subcutaneous (SQ) injection. It is important to note that the use of either form should not exceed cycle lengths of 30 days in total. After completing a cycle, it is recommended to take a minimum of 2 weeks off, although longer breaks between IGF-1 cycles are advisable. This is not only to mitigate the risk of potential health effects in the long term, but also to allow IGF-1 receptors to return to their proper working order following a cycle of usage. Proper cycling and breaks are crucial for responsible and safe use of IGF-1 LR3.
Dosage & Cycling
Dosages are as follows for IGF-1 LR3
For men, it is recommended to use no more than approximately 40 - 50mcg of IGF-1 LR3 per day, and for women, no more than 20mcg per day. Due to its long active half-life in the body, the LR3 variant should be administered once, and no more than twice per day. On workout days, it is best to administer the dose approximately 10 minutes before training or immediately after the workout. If dosing twice per day, the full daily dosage can be split in half between the two administrations (e.g. 20mcg pre-workout and 20mcg post-workout for a total of 40mcg per day). On non-training days, the dose can be administered at any time of the day.
It is important to note that IGF-1 LR3 can be used all 7 days of the week without developing desensitization, as it has a very short half-life. However, it is always recommended to follow the recommended dosages and administration guidelines to ensure responsible use and minimize the risk of potential side effects.
Dosages are as follows for IGF-1 DES
The dosage of IGF-1 DES can vary more compared to LR3, with a range of 50 - 150mcg per day. Due to its shorter half-life, higher dosages can be used with less risk of long-term effects on the body, although caution should still be exercised. Similar to IGF-1 LR3, IGF-1 DES can be used in a pre/post-workout manner, and is often utilized in this manner due to its short half-life.
Best Time To Take IGF-1
Many people prefer to consume their dose of IGF-1 after engaging in intense workout sessions.
IGF-1 Legal?
Yes!
IGF-1 is considered legal and safe for use according to the guidelines issued by the FDA, but it is typically sold for research purposes. It is important to adhere to recommended dosages and not overdose, as it may lead to clinical disorders such as acromegaly.
For more information, visit here.