A Comprehensive Guide on Depo-Testosterone
Table of Contents
Depo-Testosterone
Generic name: testosterone injection
What is Depo-Testosterone?
Depo-Testosterone is a medication used to treat conditions caused by a lack of testosterone in men and boys, such as delayed puberty, impotence, or other hormonal imbalances. It is an injectable form of testosterone cypionate that is injected into the buttock muscle and lasts for a long time, so it only needs to be used once or twice a month. It is also used in hormone therapy for transgender men.
It is a white or creamy white crystalline powder, odorless or nearly so, and stable in air. It is insoluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, chloroform, dioxane, ether, and soluble in vegetable oils.
Chemical name
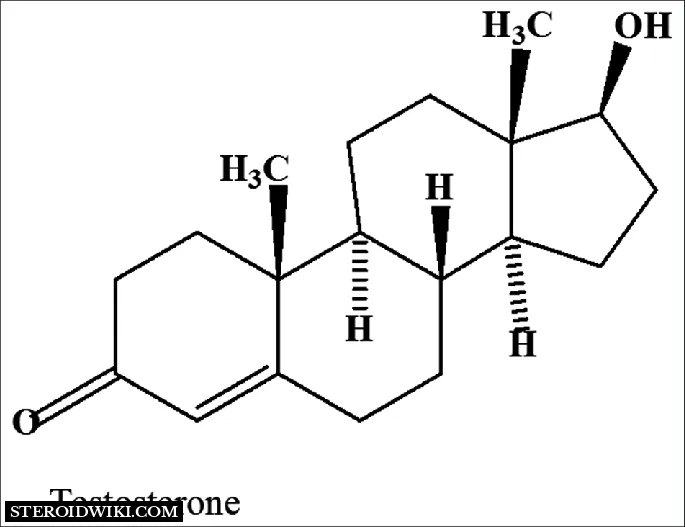
The chemical name for testosterone cypionate is androst-4-en-3-one, 17-(3-cyclopentyl1- oxopropoxy)-, (17ß)-. Its molecular formula is C27H40O3, and its molecular weight is 412.61.
The structural formula is represented below:
DEPO-Testosterone Injection

DEPO-Testosterone Injection, for intramuscular injection, contains testosterone cypionate, which is the oil-soluble 17 (beta)-cyclopentylpropionate ester of the androgenic hormone testosterone.
DEPO-Testosterone Injection is available in two strengths, 100 mg/mL and 200 mg/mL testosterone cypionate.
Each mL of the 100 mg/mL solution contains:
Testosterone cypionate: 100 mg
Benzyl benzoate: 0.1 mL
Cottonseed oil: 736 mg
Benzyl alcohol (as preservative): 9.45 mg
Each mL of the 200 mg/mL solution contains:
Testosterone cypionate: 200 mg
Benzyl benzoate: 0.2 mL
Cottonseed oil: 560 mg
Benzyl alcohol (as preservative): 9.45 mg
Indications
DEPO-Testosterone Injection is indicated for replacement therapy in the male in conditions associated with symptoms of deficiency or absence of endogenous testosterone.
- Primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired)-testicular failure due to cryptorchidism, bilateral torsion, orchitis, vanishing testis syndrome, or orchidectomy.
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) - gonadotropin or LHRH deficiency, or pituitary-hypothalamic injury from tumors, trauma, or radiation.
Uses
This medication is used in men who do not make enough of a natural substance called testosterone. In males, testosterone is responsible for many normal functions, including the growth and development of the genitals, muscles, and bones.
It also helps cause normal sexual development (puberty) in boys. Testosterone belongs to a class of drugs known as androgens. It works by affecting many body systems so that the body can develop and function normally. Testosterone may also be used in certain adolescent boys to cause puberty in those with delayed puberty. It may also be used to treat certain types of breast cancer in women.
How to use Depo-Testosterone Vial

This medication is given by injection into the buttock muscle as directed by your doctor, usually every 1 to 4 weeks. Do not inject this medication into a vein. The dosage is based on your medical condition, testosterone blood levels, and response to treatment.
Instructions
- If you are giving this medication to yourself at home, learn all preparation and usage instructions from your health care professional. Before using, check this product visually for particles or discoloration. If either is present, do not use the liquid. Learn how to store and discard medical supplies safely.
- Use this medication regularly in order to get the most benefit from it. To help you remember, use a calendar to mark the days you will receive an injection.
- Misuse or abuse of testosterone can cause serious side effects such as heart disease (including heart attack), stroke, liver disease, mental/mood problems, abnormal drug-seeking behavior, or improper bone growth (in adolescents).
- Do not increase your dose or use this drug more often or for longer than prescribed. When testosterone is misused or abused, you may have withdrawal symptoms (such as depression, irritability, and tiredness) when you suddenly stop using the drug. These symptoms may last from weeks to months.
Depo-Testosterone side effects

Safety measures
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction: hives, difficulty breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Tell your caregivers immediately if you have a tight feeling in your throat, a sudden urge to cough, or if you feel light-headed or short of breath during or shortly after receiving the injection. You will be watched closely for at least 30 minutes to make sure you do not react to the injection.
Depo-Testosterone may cause serious side effects such as:
- Chest pain or pressure, pain spreading to your jaw or shoulder
- Shortness of breath, breathing problems at night (sleep apnea)
- Swelling in your ankles or feet, rapid weight gain
- Seizure
- Unusual changes in mood or behavior
- Increased or ongoing erection of the penis, ejaculation problems, decreased amounts of semen, decrease in testicle size
- Painful or difficult urination, increased urination at night, loss of bladder control
- High levels of calcium in the blood, stomach pain, constipation, increased thirst or urination, muscle pain or weakness, joint pain, confusion, and feeling tired or restless; or High potassium level mean nausea, weakness, tingly feeling, chest pain, irregular heartbeats, loss of movement
- Liver problems. Right-sided upper stomach pain, vomiting, loss of appetite, dark urine, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
- Signs of a blood clot deep in the body swelling, warmth, or redness in an arm or leg
- Signs of a blood clot in the lung, chest pain, sudden cough, wheezing, rapid breathing, coughing up blood; or Signs of a stroke sudden numbness or weakness (especially on one side of the body), severe headache, slurred speech, balance problems.
Women receiving testosterone may develop male characteristics, which could be irreversible if treatment is continued. Call your doctor at once if you notice any of these signs of excess testosterone:
- Acne
- Changes in your menstrual periods (including missed periods)
- Male-pattern hair growth (such as on the chin or chest)
- Hoarse or deepened voice
- Enlarged clitoris.
Your Depo-Testosterones may be delayed or permanently discontinued if you have certain side effects.
Common side effects (in men or women) may include:
- Breast swelling
- Acne, increased facial or body hair growth, male-pattern baldness
- Increased or decreased interest in sex
- Headache, anxiety, depressed mood
- Increased blood pressure
- Numbness or tingly feeling
- Abnormal liver function tests
- High red blood cell counts (hematocrit or hemoglobin)
- Increased PSA (prostate-specific antigen)
- Pain, bruising, bleeding, redness, or a hard lump where the medicine was injected.
Warnings

You should not be treated with testosterone if you have prostate cancer, male breast cancer, a serious heart condition, severe liver or kidney disease, or an allergy to castor oil or sesame oil. Depo-testosterone is not for use in treating low testosterone without certain medical conditions or due to getting older. Testosterone should not be used to enhance athletic performance.
Depo-Testosterone is not for use in women who are pregnant. It can increase your risk of heart attack, stroke, or death. You may need to stop using testosterone or start taking blood pressure medication. Misuse of testosterone can cause dangerous or irreversible effects.
Before taking this medicine
You should not be treated with this medicine if you are allergic to testosterone, or if you have:
- Male breast cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Serious heart problems
- Severe liver disease
- Severe kidney disease
- An allergy to castor oil or sesame oil
Depo-Testosterone is not for use in women who are pregnant. This medicine can harm an unborn baby.
Tell your doctor if you have ever had:
- High blood pressure
- Heart problems, coronary artery disease (clogged arteries)
- Heart attack or stroke
- Sleep apnea
- An enlarged prostate and urination problems
- High cholesterol or triglycerides
- Cancer
- Depression, anxiety, a mood disorder, suicidal thoughts or actions
- Diabetes
- High red blood cell (RBC) counts
- Liver or kidney disease
Using testosterone may increase your risk of developing prostate cancer, liver problems, or heart problems (including heart attack, stroke, or death).
Women using testosterone should not breastfeed. Testosterone should not be given to a child younger than 12 years old. Some types of this medicine are not approved for use by anyone younger than 18 years old.
How is Depo-Testosterone given?
Testosterone is injected under the skin or into a muscle, usually given every 2 to 4 weeks. Depo-Testosterones should be given only by a healthcare professional. The length of treatment with Depo-Testosterone will depend on the condition being treated.
Testosterone can raise your blood pressure, which could increase your risk of heart attack, stroke, or death. Your blood pressure will need to be checked often. You may need to stop using testosterone or start taking blood pressure medication.
You will need frequent blood tests.
Testosterone can affect bone growth in boys who are treated for delayed puberty. Bone development may need to be checked with X-rays every 6 months during treatment. Depo-Testosterone can affect the results of certain medical tests. Tell any doctor who treats you that you are using testosterone.
Misuse of testosterone
Misuse of testosterone can cause dangerous or irreversible effects, such as enlarged breasts, small testicles, infertility, high blood pressure, heart attack, stroke, liver disease, bone growth problems, addiction, and mental effects such as aggression and violence. If you have used too much testosterone, stopping the medicine may cause unpleasant withdrawal symptoms, such as depression, tiredness, irritability, loss of appetite, sleep problems, or decreased libido.
Dosage
The suggested dosage for DEPO-Testosterone Injection varies depending on the age, sex, and diagnosis of the individual patient. The dosage of DEPO-Testosterone is adjusted according to the patient's response and the appearance of side effects.
Drugs Interaction
DEPO-Testosterone may interact with oral anticoagulants, oxyphenbutazone, and insulin. Tell your doctor about all medications and supplements you use.
References
- Aboudkhil, S., Bureau, J.P., Garrelly, L. and Vago, P., 1991. Effects of castration, Depo‐testosterone and cyproterone acetate on lymphocyte T subsets in mouse thymus and spleen. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology, 34(5), pp.647-653.
- Guthrie, R.D., Smith, D.W. and Graham, C.B., 1973. Testosterone treatment for micropenis during early childhood. The Journal of Pediatrics, 83(2), pp.247-252.
- Luthy, K.E., Williams, C., Freeborn, D.S. and Cook, A., 2017. Comparison of testosterone replacement therapy medications in the treatment of hypogonadism. The Journal for Nurse Practitioners, 13(4), pp.241-249.
- Kravitz, H.M., Haywood, T.W., Kelly, J., Liles, S. and Cavanaugh, J.L., 1996. Medroxyprogesterone and paraphiles: Do testosterone levels matter?. Journal of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law Online, 24(1), pp.73-83.
- Depo-Testosterone Intramuscular: Uses, Side Effects, Interactions, Pictures, Warnings & Dosing WebMD. WebMD. Available at: https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-11771/depo-testosterone-intramuscular/details (Accessed: 30 January 2024).
- Depo-Testosterone Uses, Side Effects & Warnings Drugs.com. Available at: https://www.drugs.com/mtm/depo-testosterone.html (Accessed: 30 January 2024).
Disclaimer: SteroidWiki doesn’t promote unlawful usage of any chemical compound. The knowledge presented in this article and on the website is purely for educational purposes. If you intend to use the information provided in this article for any purpose, please make sure to check & comply with the laws of your country or area.