Understanding Testosterone Cypionate: A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
Testosterone Cypionate is a drug classified as androgens and anabolic steroids that is primarily used to treat male testosterone shortage. This page provides a complete overview of Testosterone Cypionate, including its description, clinical pharmacology, indications and usage, contraindications, warnings, precautions, dose and administration, and more.
Description
Testosterone Cypionate injectable, USP is an intramuscular injectable that includes the active component Testosterone Cypionate, USP. This chemical is a white or creamy white crystalline powder with a low odour that is stable in air but insoluble in water. It is soluble in alcohol, chloroform, dioxane, ether, and certain vegetable oils.
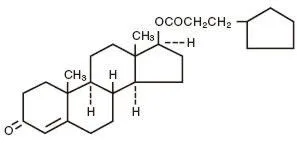
Testosterone Cypionate, USP's chemical name is androst-4-en-3-one,17-(3-cyclopentyl-1-oxopropoxy)-, (17β)-, with a molecular formula of C27H40O3 and a molecular weight of 412.61.
Each millilitre of the 200 mg/mL solution includes 200 mg of Testosterone Cypionate, USP, as well as preservatives such as benzyl benzoate, cottonseed oil, and benzyl alcohol.
The structural formula is represented below:
Clinical Pharmacology
Endogenous androgens are essential for the proper growth and development of male sex organs, as well as the preservation of secondary sex characteristics. Testosterone Cypionate works by imitating the effects of natural testosterone. It helps to develop and maintain a variety of masculine traits, including genital growth, face and body hair, voice deepening, and muscular development.
According to pharmacokinetic research, testosterone esters have a lower polarity than free testosterone. When injected intramuscularly, testosterone cypionate is slowly absorbed from the lipid phase, allowing for two to four weeks between doses. Approximately 98% of testosterone in plasma is attached to a particular binding globulin, leaving the remaining 2% free to circulate. Metabolism happens largely in the liver, with outflow via urine and feces.
Working of Testosterone cypionate
Testosterone cypionate is a testosterone replacement that mimics the natural sex hormone. Testosterone is responsible for the development and maintenance of several masculine characteristics. It works by increasing or replacing testosterone in the body to normal and healthy levels.
Indications and Usage
Testosterone Cypionate Injection, USP is used as replacement treatment in males who have symptoms of testosterone insufficiency or absence. These disorders can include primary hypogonadism (congenital or acquired) and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (congenital or acquired).
It is crucial to highlight that the safety and efficacy of treating "age-related hypogonadism" (late-onset hypogonadism) have not been shown.
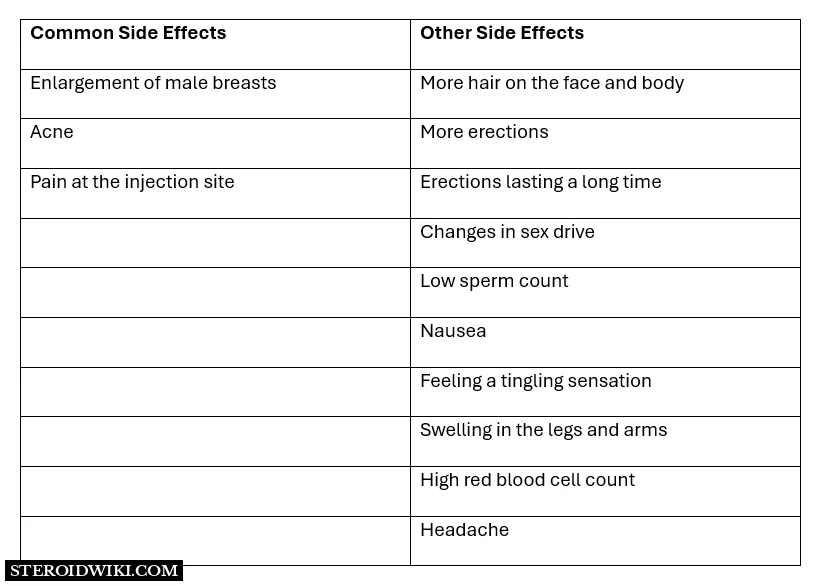
Side effects
Testosterone-CHP use does have some unwanted side effects.
It is converted to the hormone estrogen (by aromatization) by the notorious aromatize enzyme. This can cause breast tissue growth in males (gynecomastia), increased fat accumulation and decreased fat breakdown, likely loss of sex desire, practically definite testicular atrophy, and water retention. This product will most likely cause significant water retention, which might raise blood pressure and weaken blood vessels over time.
Testosterone can also interact with the 5 alpha-reductase enzyme, which transforms testosterone into Dihydro-testosterone (DHT), a stronger androgenic derivative of the parent hormone. This novel chemical has a high binding affinity for scalp tissues, causing hair loss in individuals with male pattern baldness. DHT can affect the prostate as well, making it swell. This swelling can cause the gland to press against the bladder causing urinary problems, especially urinary difficulty
Contraindications and Warnings
Testosterone Cypionate is not recommended for those who have a known hypersensitivity to the medicine, men who have breast or prostate cancer or pregnant women owing to the possibility of fetal injury. It's also not recommended for those who have major cardiac, hepatic, or renal disorders.
Warnings about Testosterone Cypionate include the danger of hypercalcemia in immobilized individuals, hepatic consequences from sustained high dosages, an increased risk of prostate problems in senior people, and reports of venous thromboembolic events. Long-term cardiovascular safety studies have not been undertaken, and testosterone misuse can result in significant side effects.
Precautions
Patients with benign prostatic enlargement should take extra measures to avoid acute urethral blockage. Priapism, increased sexual excitement, and oligospermia are all possible side effects. Testosterone Cypionate and testosterone propionate should not be used interchangeably owing to variances in action duration.
Patients should be educated about potential adverse effects and encouraged to report any symptoms as soon as possible. It is recommended to check haemoglobin, hematocrit, and serum cholesterol levels on a regular basis.
Dosage and Administration
The dose of testosterone cypionate varies according to the patient's age, gender, and diagnosis. It should be injected intramuscularly, deep into the gluteal muscle. Dosage regimes may need to be changed depending on individual responses and the occurrence of adverse effects.
Replacement treatment doses in hypogonadal males normally vary from 50 to 400 mg every two to four weeks. Parenteral medication products should be visually scrutinized for particle matter and discoloration before to delivery.
Conclusion
Testosterone Cypionate is an important ingredient in the treatment of testosterone insufficiency in men. Understanding its pharmacological features, indications, contraindications, and dosing instructions is critical for safe and successful usage. Patients taking Testosterone Cypionate medication should be constantly monitored by healthcare practitioners, who should also educate them on potential side effects and precautions. Healthcare providers can ensure optimal treatment outcomes while reducing the dangers associated with testosterone replacement therapy by adhering to correct prescription standards.
References
- Pan, M.M. and Kovac, J.R., 2016. Beyond testosterone cypionate: evidence behind the use of nandrolone in male health and wellness. Translational Andrology and Urology, 5(2), p.213.
- Testosterone cypionate (Depo-Testosterone): Uses, Side Effects, Dosage & Reviews (no date) GoodRx. Available at: https://www.goodrx.com/testosterone-cypionate/what-is (Accessed: 1 March 2024).
- Behre, H.M., Wang, C., Handelsman, D.J. and Nieschlag, E., 2004. Pharmacology of testosterone preparations. Testosterone, action, deficiency, substitution, pp.405-444.
- Steroid.com. Available at: https://www.steroid.com/Testosterone-CHP.php (Accessed: 1 March 2024).
- Choi, E.J., Xu, P., Barham, D., El-Khatib, F.M., Yafi, F.A. and Kavoussi, P.K., 2022. Comparison of outcomes for hypogonadal men treated with intramuscular testosterone cypionate versus subcutaneous testosterone enanthate. The Journal of Urology, 207(3), pp.677-683.